how do umbilical cord work
Home How Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Works. Both bring blood to your child.

True Knot In Umbilical Cord Risk Factors Signs Diagnosis And Treatment
After birth the umbilical cord is no longer needed so its clamped and snipped.

. After that your job is to focus on bringing your baby into the world while. One branch returns to your stomach while the other leads directly to your baby. What Is an Umbilical Cord.
The veins job is to transport oxygen and nutrients from your placenta to your baby. It delivers vital nutrients from your body to your baby and ferries away the waste products your baby produces. It attaches to the placenta an organ grown specifically for your babys birth.
The umbilical cord will eventually be responsible for funneling all the nutrients and oxygen from the mother to the fetus so its a critical time. The tissue surrounding the umbilical vein and arteries acts like a cushion preventing twisting and compression to ensure the cord blood flow remains steady and. The umbilical cord is still tied to your kid within your womb when his or her head emerges from your vagina.
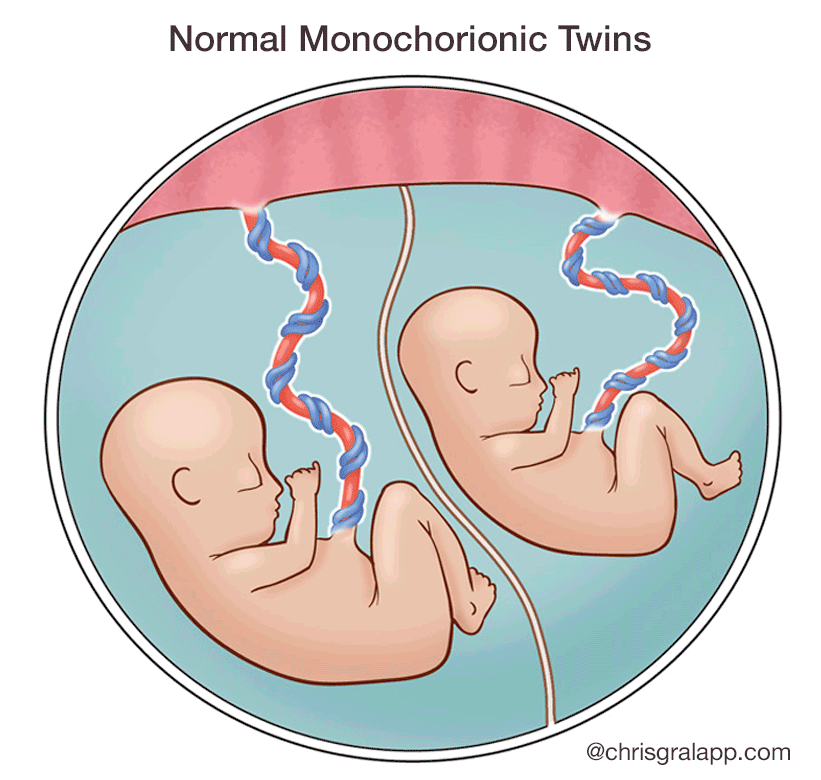
Human umbilical cord is attractive source for autologous and allogenic stem cells that are currently amenable to treatment of various diseases. But its possible to have either multiple or single placentas depending on exactly how the development process goes. During pregnancy the umbilical cord supplies nutrients and oxygen to your developing baby.
During pregnancy the umbilical cord supplies nutrients and oxygen to your developing baby. In doing so it also functions to remove waste products from fetal circulation. The umbilical cord is a fetal organ connecting the placenta to the developing fetus.
The umbilical cord and the fetal portion of the placenta is an organ that grows from the fetus. In the human fetus the umbilical cord arises at the belly and by the time of birth is about 2 feet 60 cm long and 05 inch 13 cm in diameter. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated nutrient-rich blood.
The umbilical cord emerges from the remnants of the yolk sac and the allantois which handles the embryos waste. Umbilical cord blood banking is actually a simple painless process for mother and baby. When umbilical cord cells are placed into an environment of injured or diseased tissue the stem cells go to work inhibiting the damaging inflammatory components and modulating the immune system.
The cord lets baby stay attached to the placenta with plenty of room to move and grow. During prenatal development the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and normally contains two arteries and one vein buried within Whartons jelly. Your babys umbilical cord connects from their navel to the placenta a special organ that grows during pregnancy to facilitate moving blood oxygen and nutrients from you to your baby.
The pups will develop and grow inside the mother and they will feed and receive oxygen through a specialized embryonic organ which is called the umbilical cord. All dogs will be born with an umbilical cord and this has a really important function. The umbilical chord splits into two branches after it passes through your pelvic canal.
Umbilicals connect from the surface facility to the subsea development through an Umbilical Termination Structure UTS. The umbilical cord starts to form at about 4 weeks of pregnancy. During pregnancy the umbilical cord is your babys lifeline to the placenta the pancake-shaped organ attached to your uterus.
After birth the umbilical cord is no longer needed so its clamped and snipped. What Does a Dogs Umbilical Cord Do. Your babys umbilical cord connects to the placenta allowing this exchange of oxygenated blood via the umbilical vein.
This cord is attached to the mothers placenta. Learn all you need to know about umbilical cord blood banking and why Cord for Life is the best program for you. Discover How Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Works from Cord for Life.
It contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein through which the fetal heart pumps blood to and from the placenta in which exchange of nutrient and waste materials with the circulatory system of the mother takes place. At full-term it contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. What is the umbilical cord.
The arteries are responsible for transporting your babys waste material which are eventually disposed of through your. This leaves behind a short stump. On average its 20 inches long.
Umbilical Cord Care Cord of Life For eight or so months the umbilical cord which forms around five weeks gestation carries nutrients and oxygen from you to your baby and delivers deoxygenated blood and waste back to the placenta. The plethora of regenerative cells in postnatal tissues including umbilical cord amniotic fluid and placenta consist of growth factors stem cells exosomes secretomes cytokines and. In placental mammals the umbilical cord is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta.
Each will have their own that then connects to the maternal placenta. The umbilical cords arteries and veins are surrounded by a. Stem cells have currently gained attention in the field of medicine not only due to their ability to repair dysfunctional or damaged cells but also they could be used as drug delivery system after being engineered to do so.
What is the use of the umbilical cord. This structure allows for the passage of oxygen and nutrients from the maternal circulation to the fetal circulation. The umbilical cord carries oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetus through the abdomen where the navel forms.
The most important part is to be sure to order a Collection Kit in advance and bring it with you to the hospital when you go into labor. Furthermore these cells secrete growth factors and other products that nourish damaged cells back to health and stimulate the bodys own cells to regenerate themselves.

What Is The Umbilical Cord Babycenter

What Is The Difference Between Placenta And Umbilical Cord Quora
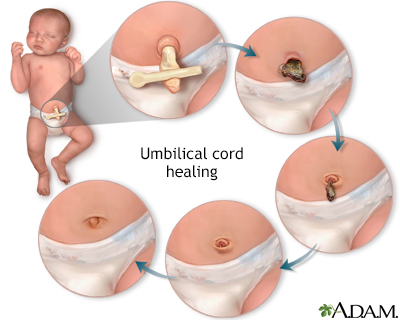
Umbilical Cord Care In Newborns Information Mount Sinai New York
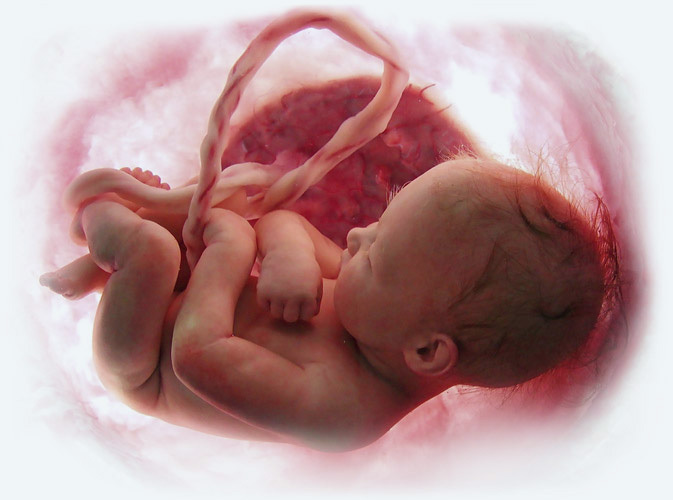
10 Reasons For Umbilical Cord Blood And Tissues Collection Cord Blood Center Group
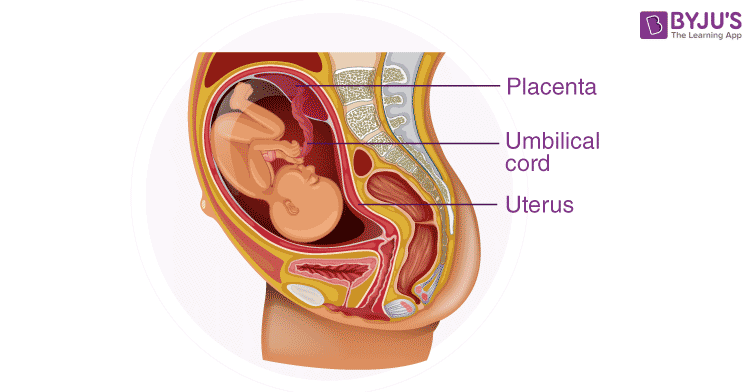
Difference Between The Placenta And Umbilical Cord
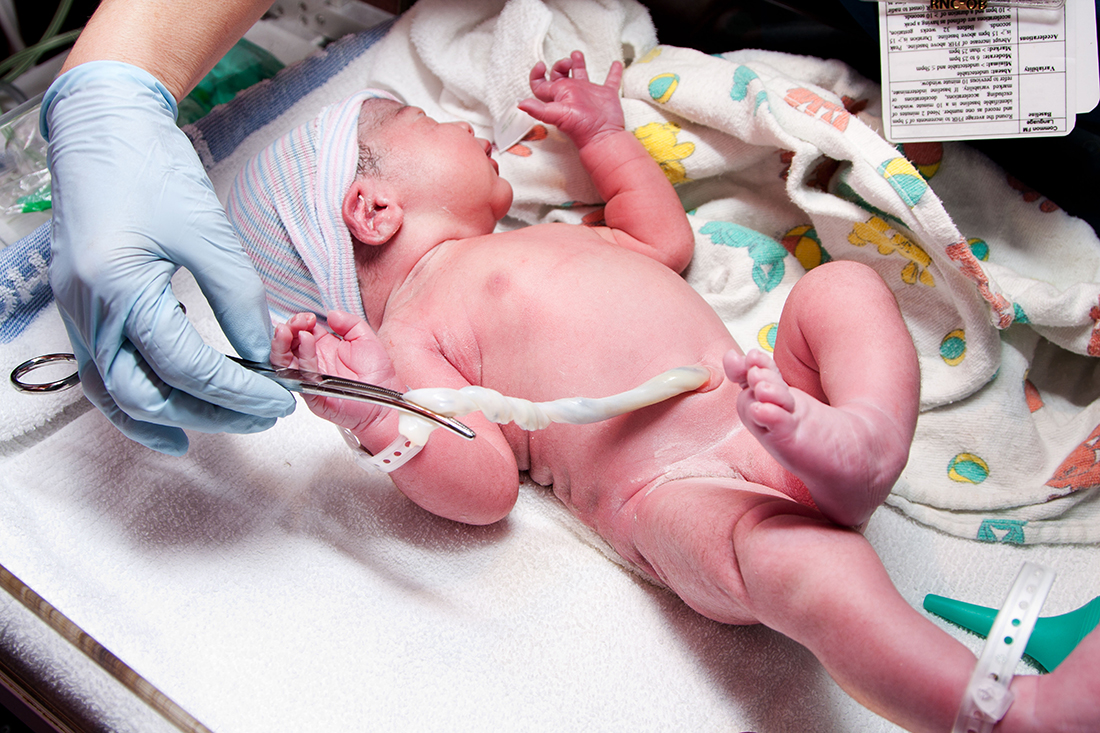
Lotus Birth What Experts Say About Cutting The Cord Live Science
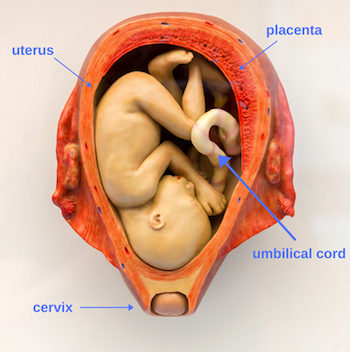
Velamentous Cord Insertion Marginal Cord Insertion Risks

What Are Signs Of Umbilical Cord Problems Brown Trial Firm

Types Of Umbilical Cord Problems
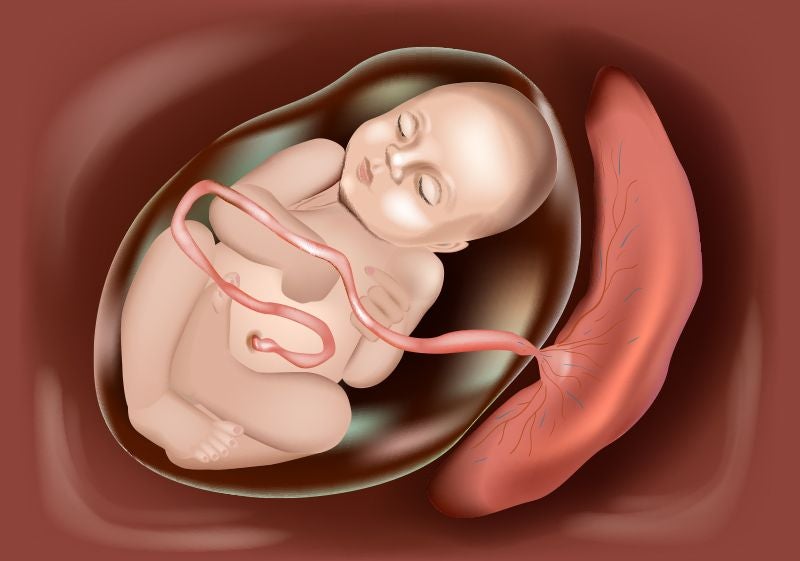
Umbilical Cord Vs Placenta Difference Between Placenta And Umbilical Cord
Hie Multimedia Kids Umbilical Cord

What Is The Umbilical Cord Babycenter
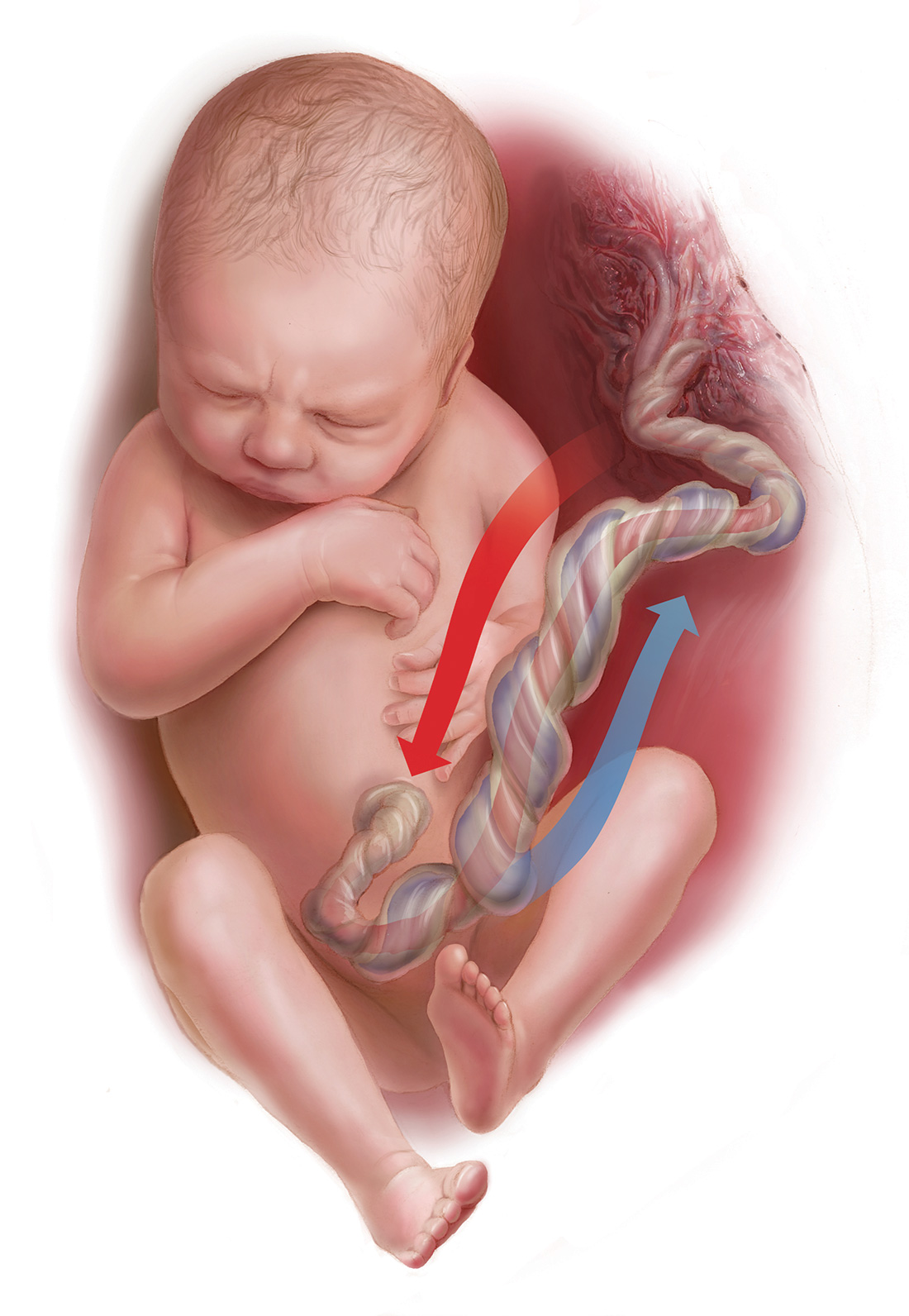
How And When Umbilical Cord Gas Analysis Can Justify Your Obstetric Management Mdedge Obgyn

Function Of Umbilical Cord A Detailed Guide For Parents
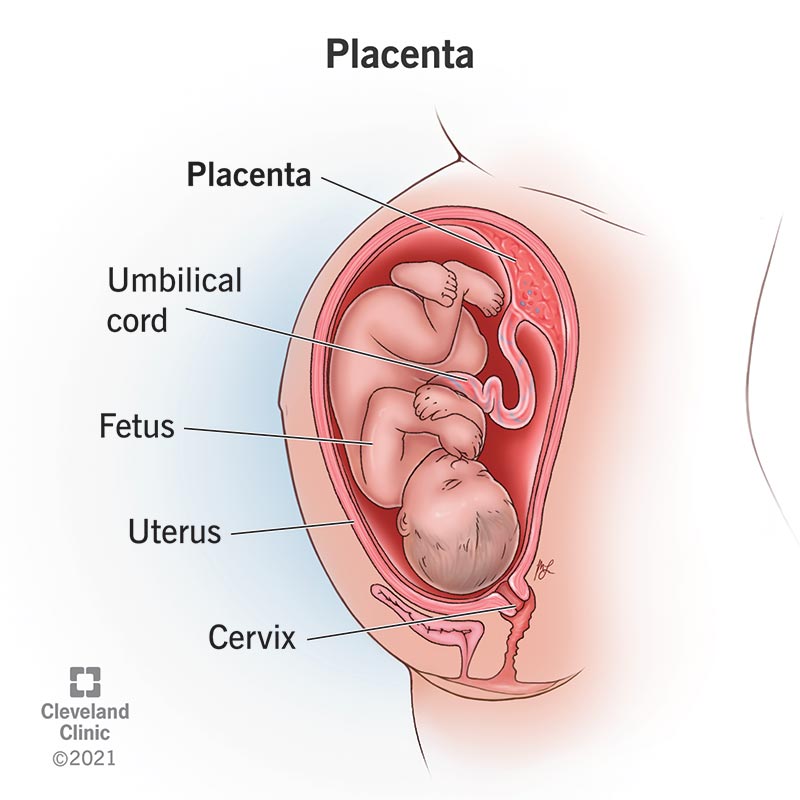
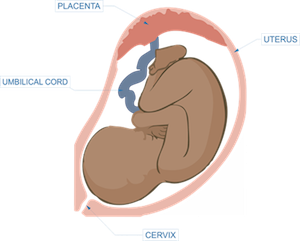
Placenta Overview Anatomy Function Complications
How Did Doctors Create My Belly Button Science Questions With Surprising Answers
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1202710980-c04fac86a3434095b31e4472674da83d.jpg)